Share Data between Docker Containers
There are three types of data to manage data in Docker,
- bind mount
- volume mount
- tmpfs mount
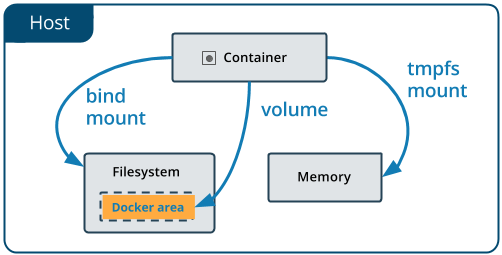
Read Manage data in Docker for more information, it's a great official documentation!
Here, this page demonstrates some use cases in practices that you maybe face. As the official documentation says, Volume is alway the first choice and preferred mechanism for persisting and sharing data between containers, as one of the biggest advantages is that volume is thoroughly managed by Docker. That means:
- You can manage volume using Docker CLI commands ir the Docker API.
- Volume is easier to back up and migrate than bind mounts.
- Volume work the same interface in Linux and Windows, such as no need to worry about
POSIXfile path style in Windows. - Volume driver features support you to store data on remote hosts or cloud storage easily.
- Volume on Docker Desktop have much higher performance than bind mount from Mac and Windows hosts.
Let's look at some use cases that leverage volume driver features
Use a volume to bind a local folder
In default, the volume is created by Docker and its corresponding folder resides in Docker managed folder like /var/lib/docker/volumes/:
$ docker create volume xxx
$ docker volume inspect xxx
[
{
"CreatedAt": "2023-07-19T14:41:18+08:00",
"Driver": "local",
"Labels": {},
"Mountpoint": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/xxx/_data",
"Name": "xxx",
"Options": {},
"Scope": "local"
}
]
However, sometimes you would like to bind the volume into a specified local folder(like /data/volumes/testvol) in hosts(only available in Linux)
$ docker volume create --opt type=none --opt o=bind --opt device=/data/volumes/testvol testvol
$ docker inspect testvol
[
{
"CreatedAt": "2023-07-13T04:36:16Z",
"Driver": "local",
"Labels": {},
"Mountpoint": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/testvol/_data",
"Name": "testvol",
"Options": {
"device": "/data/volumes/testvol",
"o": "bind",
"type": "none"
},
"Scope": "local"
}
In Docker compose yaml,
services:
frontend:
image: node:lts
volumes:
- testvol:/home/node/app
volumes:
db-data:
testvol:
driver: local
driver_opts:
type: none
o: bind
device: /data/volumes/testvol